
Sleep is a complex and dynamic process that affects how you function in ways scientists are now beginning to understand. Research shows that a chronic lack of sleep, or getting poor quality sleep, increases the risk of disorders including high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, depression, and obesity. Sleep affects almost every type of tissue and system in the body – from the brain, heart, and lungs to metabolism, immune function, mood, and disease resistance. Recent findings suggest that sleep plays a housekeeping role that removes toxins in your brain that build up while you are awake.Įveryone needs sleep, but its biological purpose remains a mystery. In fact, your brain and body stay remarkably active while you sleep. Sleep is important to a number of brain functions, including how nerve cells (neurons) communicate with each other. Without sleep you can’t form or maintain the pathways in your brain that let you learn and create new memories, and it’s harder to concentrate and respond quickly. Quality sleep – and getting enough of it at the right times - is as essential to survival as food and water. NURSE-ON-CALL Tel.Sleep is an important part of your daily routine-you spend about one-third of your time doing it.Australasian Sleep Association External Link.periodic limb movement disorder and restless legs syndrome.

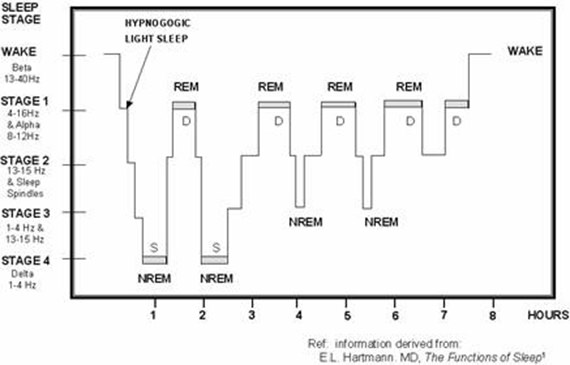
Most dreams are thought to occur during REM sleep. The sleeper’s eyes tend to dart about under closed lids, hence the name. The brain in REM sleep shows significant electrical activity. It makes up about one-quarter of your night’s sleep. Rapid eye movement sleep occurs regularly during sleep, about once every 90 to 120 minutes. The two broad categories of sleep include: The brain moves through distinct stages of sleep, over and over, every night. Sleep isn’t a static (unchanging) state of consciousness. New parents lose, on average, between 450 and 700 hours of sleep during their child’s first 12 months of life. Studies show that common distractions from sleep are: It is thought that sleepiness causes about one road accident in six. Most of us feel that we haven’t had enough sleep at least some of the time. The Sleep Health Foundation recommends that adults should aim for 7–9 hours of sleep per night. Today, sleep deprivation is common in developed nations, with the average adult sleeping for only six or seven hours each night. In the morning, exposure to daylight suppresses these hormones and releases brain chemicals to keep you awake. When the sun sets, your brain releases hormones to make you sleepy. The body’s internal clock regulates when and how we sleep depending on the amount of light around us. Lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation, can cause fatigue, poor concentration and memory, mood disturbances, impaired judgement and reaction time, and poor physical coordination. It refreshes the mind and repairs the body. Most scientists agree that sleep is important for restoring physical and mental health. Sleep is as essential for good health as oxygen, food and water.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
